Introduction
As we are getting continuous queries on Fraud Risk Management, we decided to publish a series of short guidelines related to this topic. In this first guide, we will underline the important general explanation around the concept, with some examples. Following series will be discussions around different sectors and fraud risk types.
Reach out to βrazan for effective strategies to combat with fraud.

Fraud risk management is a critical aspect of organizational governance, aiming to protect assets, ensure compliance, and uphold the integrity of operations. This guide provides a thorough overview of the fraud risk management cycle, detailing practical steps and offering examples for different fraud risks encountered during assessments.
Fraud Risk Management Cycle
The fraud risk management cycle is an iterative process that involves several steps to identify, assess, respond to, and monitor fraud risks within an organization. This cycle ensures continuous improvement and adaptation to emerging risks.
Establish a Risk Management Group and Set Goals
- Form a team comprising key personnel such as the Chief Risk Officer, internal auditors, finance directors, and operational staff.
- Define the objectives of the risk management process and ensure alignment with the organization’s overall strategy
Identify Risk Areas
- Conduct workshops, interviews, brainstorming sessions, and process mapping to uncover potential fraud risks across all business areas
- Use techniques such as comparisons with other organizations and discussions with peers to enhance the identification process
Understand and Assess the Scale of Risk
- Evaluate the potential impact and likelihood of identified risks using a consistent framework.
- Consider both financial and non-financial impacts, such as reputational damage.
Develop a Risk Response Strategy
- Create strategies to address each identified risk, which may include risk retention, risk avoidance, risk reduction, and risk transfer
- Establish the organization’s risk appetite to guide the development of these strategies
Implement the Strategy and Allocate Responsibilities
- Assign specific responsibilities to operational managers and set clear target dates for action.
- Ensure that those responsible for implementing the strategy are adequately informed and motivated through formal communication and training sessions.
Implement and Monitor Suggested Controls
- Introduce or modify controls to mitigate identified risks.
- Continuously monitor the effectiveness of these controls and adjust them as necessary based on internal and external factors.
Review and Refine the Process
- Regularly review the entire risk management process to identify areas for improvement.
- Integrate risk management into the organization’s culture, making it a part of everyone’s responsibilities.
Practical Steps in Fraud Risk Management
Conducting Fraud Risk Assessments
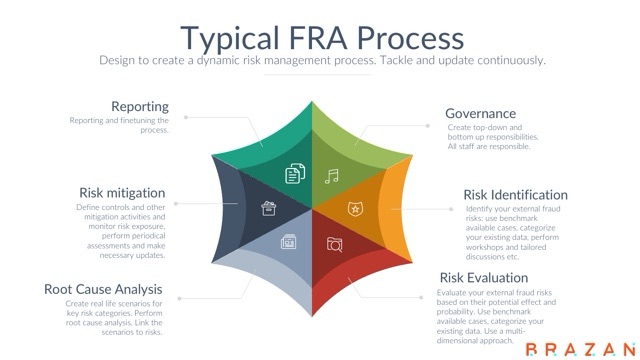
- Perform detailed fraud risk assessments to uncover previously unidentified risks and strengthen prevention and detection capabilities.
- Use qualitative and quantitative methods to evaluate the likelihood and impact of fraud risks .
Developing Anti-Fraud Policies
- Establish clear anti-fraud policies and procedures, including codes of ethics and whistleblower protections.
- Ensure that these policies are regularly reviewed and communicated across the organization .
Fraud Risk Training and Awareness
- Implement comprehensive fraud risk training programs for all employees, focusing on high-risk areas such as procurement and financial transactions.
- Utilize various communication methods, including formal training sessions, newsletters, and internal websites, to raise awareness.
Monitoring and Detection Techniques
- Utilize advanced tools such as data mining, trend analysis, and exception reporting to detect potential fraud.
- Regularly update fraud detection systems to keep pace with evolving fraud tactics.
Investigating Fraud
- Establish clear procedures for investigating suspected fraud, including documenting findings and taking corrective action.
- Ensure that investigations are conducted thoroughly and impartially to maintain trust and integrity within the organization.
Sample Fraud Risk Assessments
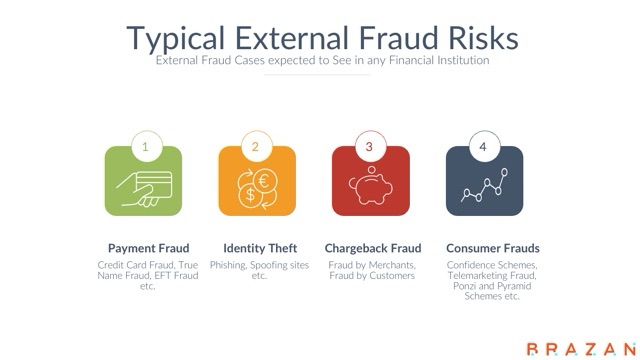
Procurement Fraud
- Risk: Unauthorized purchase orders leading to financial loss.
- Likelihood: High, due to lack of segregation of duties.
- Impact: Significant financial loss and reputational damage.
- Controls: Implement strict approval processes and regular audits.
- Action: Immediate review and enhancement of procurement controls.
Payroll Fraud
- Risk: Fictitious employees receiving salaries.
- Likelihood: Medium, due to inadequate employee verification processes.
- Impact: Moderate financial loss and operational inefficiencies.
- Controls: Conduct periodic payroll audits and implement biometric verification.
- Action: Regular audits and updates to verification procedures.
Cyber Fraud
- Risk: Unauthorized access to sensitive information via phishing attacks.
- Likelihood: High, due to increasing sophistication of cyber-attacks.
- Impact: Severe financial and reputational damage.
- Controls: Enhance cybersecurity measures, conduct regular training, and implement multi-factor authentication.
- Action: Continuous monitoring and updates to cybersecurity protocols.
Conclusion
Effective fraud risk management requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses identification, assessment, response, and continuous monitoring. By establishing robust policies, fostering a culture of awareness, and utilizing advanced detection tools, organizations can significantly mitigate the risk of fraud and protect their assets and reputation.

Leave a comment